Когда мы только начинаем изучать Python, мы закладываем некоторые вредные привычки при написании кода, о которых мы можем даже не подозревать.

10 ошибок в Python, которые делают новички
Вы можете написать код, который сработает сейчас, но может не сработать в будущем, или вы можете использовать какие-то хитрые ходы вместо встроенной функции, которая могла бы облегчить вашу жизнь.
У большинства из нас сохранились не одна из тех вредных привычек при программировании на Python, что формируются в период первых месяцев обучения. Отличная новость в том, что вы можете с легкостью искоренить их, прочитав приведенный ниже текст.
1. Использование import *
Каждый раз, когда нам становится лень, то возникает соблазн импортировать все необходимое из модуля с помощью from xyz import *.
Это не самый лучший подход по многим причинам. Кот несколько из них:
- Это может оказаться неэффективно: если в модуле очень много объектов, то вам придется долго ждать, пока все импортируется.
- Это может вызвать конфликт имен переменных: когда вы используете
*, то вы понятия не имеете, какие объекты вы импортируете и как они называются.
Как же с этим бороться? Импортируйте либо какой-то конкретный объект, либо весь модуль целиком.
# Using import * # Bad from math import * print(floor(2.4)) print(ceil(2.4)) print(pi) # Good import math from math import pi print(math.floor(2.4)) print(math.ceil(2.4)) print(pi)
2. Try/except: отсутствие указания исключения в блоке «except»
Я очень долго пренебрегал этим. Сложно посчитать, сколько раз Pycharm давал мне понять (этими противными подчеркиваниями), что не нужно использовать «голое» исключение. Это идет в разрез с рекомендациями PEP8.
# Try - except
# Bad
try:
driver.find_element(...)
except:
print("Which exception?")
# Good
try:
driver.find_element(...)
except NoSuchElementException:
print("It's giving NoSuchElementException")
except ElementClickInterceptedException:
print("It's giving ElementClickInterceptedException")
Проблема «голых» исключений заключается в том, что оно будет перехватывать исключения SystemExit и KeyboardInterrupt, что затрудняет прерывание программы с помощью Control-C.
В следующий раз, когда вы будете использовать try/except, укажите исключение в блоке except.
3. Не использовать Numpy для математических вычислений
Очень часто мы забываем, что в Python есть множество пакетов, которые могут значительно облегчить нашу жизнь и сделать ее более продуктивной.
Одним из таких пакетов является Numpy – пакет для математических вычислений. Numpy может помочь вам вычислять математические операции быстрее, чем циклы for.
Допустим, что у нас есть массив random_scores, и мы хотим получить средний балл тех, кто не сдал экзамен (score<70). Теперь попробуем решить это с помощью цикла for.
import numpy as np
random_scores = np.random.randint(1, 100, size=10000001)
# Bad (solving problem with a for loop)
count_failed = 0
sum_failed = 0
for score in random_scores:
if score < 70:
sum_failed += score
count_failed += 1
print(sum_failed/count_failed)
А теперь давайте решим это с помощью Numpy.
# Good (solving problem using vector operations) mean_failed = (random_scores[random_scores < 70]).mean() print(mean_failed)
Если вы запустите оба варианта, то увидите, что Numpy работает быстрее. Почему? Потому что Numpy распараллеливает наши операции.
4. Не закрываете ранее открытый файл
Обычная практика, которую знают все, заключается в том, что каждый файл, который мы открываем с помощью Python, должен быть закрыт.
Вот почему мы используем open, write/read, close каждый раз при работе с файлами. Это нормально, но если методы write/read генерируют исключение, то файл закрыт не будет.
Для того, чтобы избежать данной проблемы, мы должны использовать оператор with. Это закроет файл, даже если есть исключение.
# Bad
f = open('dataset.txt', 'w')
f.write('new_data')
f.close()
# Good
with open('dataset.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('new_data')
5. Несоблюдение рекомендаций PEP8
PEP8 – это документ, который должен прочитать каждый, кто изучает Python. В нем содержатся руководящие принципы и методические рекомендации по написанию программного кода на Python (некоторые рекомендации в этой статье взяты именно из PEP8).
Это руководство может немного напугать новичков в Python. К счастью, некоторые правила PEP8 уже встроены в IDE (именно так я и узнал о правиле, касающемся «голого» исключения).
Допустим, что вы используете Pycharm. Если вы начнете писать код, который не соответствует рекомендациям РЕР8, то вы увидите эти противные подчеркивания как на картинке ниже.
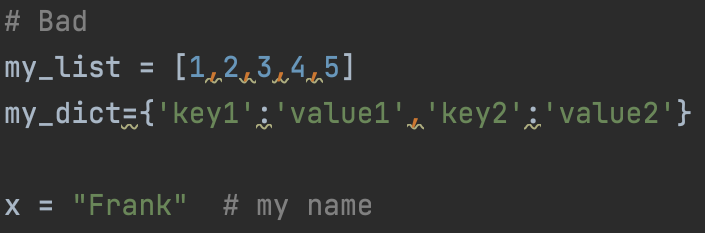
Если вы наведете курсор на подчеркивание, то увидите инструкции по исправлению.
В моем случае мне нужно только добавить пробелы после запятых и двоеточий.
# Good
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
my_dict = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
my_name = "Frank"
Я также изменил имя моей переменной x на my_name. Для Pycharm это не так важно, но РЕР8 рекомендует использовать имена переменных, по которым легко понять, что она обозначает.
6. Неправильное использование методов .keys и .values при работе со словарями
Думаю, что многие из вас знают, что делают методы .keys и .values при работе со словарями.
Если все же не знаете, то давайте посмотрим.
dict_countries = {'USA': 329.5, 'UK': 67.2, 'Canada': 38}>>>dict_countries.keys()
dict_keys(['USA', 'UK', 'Canada'])>>>dict_countries.values()
dict_values([329.5, 67.2, 38])
Проблема тут заключается в том, что мы не всегда используем их должным образом.
Например, мы хотим просмотреть словарь и получить ключи. Вы можете использовать метод .keys, но знаете ли вы, что ключи можно получить, просто перебирая словарь? В этом случае использование метода .keys будет излишним.
# Not using .keys() properly
# Bad
for key in dict_countries.keys():
print(key)
# Good
for key in dict_countries:
print(key)
Кроме того, можно придумать некоторые хитрости для получения значений словаря, например, с помощью метода .items().
# Not using .items()
# Bad
for key in dict_countries:
print(dict_countries[key])
# Good
for key, value in dict_countries.items():
print(key)
print(value)
7. Никогда не использовать генераторы (или использовать их всегда)
Генератор предлагает более простой синтаксис при создании новой последовательности (списка, словаря и т.д.) на основе уже определенной последовательности.
Допустим, мы хотим перевести все элементы в нашем списке countries в нижний регистр.
И хотя вы могли бы это сделать просто с помощью цикла for, но также вы можете упростить работу при помощи генератора списка.
# Bad
countries = ['USA', 'UK', 'Canada']
lower_case = []
for country in countries:
lower_case.append(country.lower())
# Good (but don't overuse it!)
lower_case = [country.lower() for country in countries]
Генераторы – это очень полезно, но не злоупотребляйте ими! Помните правило Дзен Python: «Простое лучше, чем сложное».
8. Использование range(len())
Одни из первых функций, которые мы изучили будучи новичками – это range и len, поэтому не удивительно, почему многие люди имеют дурную привычку писать range(len()) при переборе списков.
Допустим у нас есть два списка: countries и populations. Если мы хотим пройтись по обоим спискам одновременно, то, вероятнее всего, вы воспользуетесь range(len()).
# Using range(len())
countries = ['USA', 'UK', 'Canada']
populations = [329.5, 67.2, 38]
# Bad
for i in range(len(countries)):
country = countries[i]
population = populations[i]
print(f'{country} has a population of {population} million people')
И хотя это в принципе выполняет свою работу, вы все равно можете упростить задачу, воспользовавшись enumerate (или, что еще лучше, воспользовавшись функцией zip для сопряжения элементов из обоих списков).
# OK
for i, country in enumerate(countries):
population = populations[i]
print(f'{country} has a population of {population} million people')
# Much Better
for country, population in zip(countries, populations):
print(f'{country} has a population of {population} million people')
9. Форматирование с помощью оператора +
Вероятно, одна из первых вещей, которую мы изучаем в Python, - это то, как соединять строки с помощью оператора +.
Это полезный, но не самый эффективный способ соединения строк в Python. Помимо этого, это не очень красиво – чем больше строк вам нужно соединить, тем больше операторов + вы будете использовать.
Вместо этого вы можете воспользоваться f-строкой.
# Formatting with + operator
# Bad
name = input("Introduce Name: ")
print("Good Morning, " + name + "!")
# Good
name = input("Introduce Name: ")
print(f'Good Morning, {name}')
Преимуществом f-строк в том, что они полезны не только для конкатенации, но и для других целей.
10. Использование изменяемых значений в качестве значений по умолчанию
Если вы включите изменяемое значение (например, список) в качестве параметра функции по умолчанию, то увидите нечто неожиданное.
# Bad
def my_function(i, my_list=[]):
my_list.append(i)
return my_list>>> my_function(1)
[1]
>>> my_function(2)
[1, 2]
>>> my_function(3)
[1, 2, 3]
В приведенном выше коде каждый раз, когда мы вызываем функцию my_function, список my_list сохраняет значения из предыдущих вызовов (а мы, скорее всего, хотим инициировать пустой список при каждом вызове функции).
Чтобы избежать такой проблемы, мы должны установить этот параметр my_list равным None и добавить условие if как показано ниже.
# Good
def my_function(i, my_list=None):
if my_list is None:
my_list = []
my_list.append(i)
return my_list>>> my_function(1)
[1]
>>> my_function(2)
[2]
>>> my_function(3)
[3]